Exploring Liposome-Chitosan and Liposome-Xanthan Gum Interactions
Author:
Charles White ’25Co-Authors:
Faculty Mentor(s):
Kenneth, Mineart, Chemical EngineeringFunding Source:
College of EngineeringAbstract
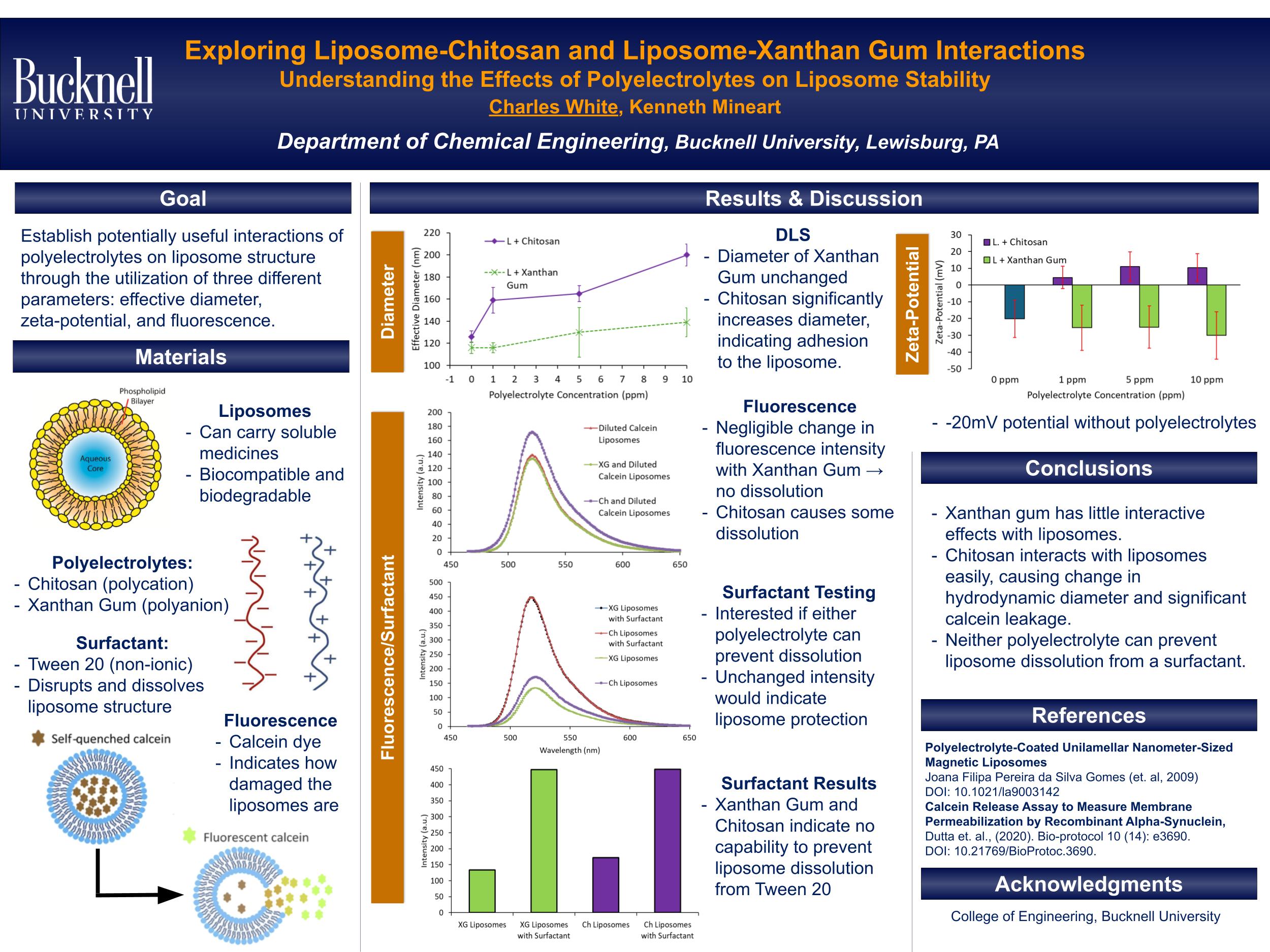
My work investigates the interactions between liposomes and two polyelectrolytes with opposing charges: chitosan, a polycation, and xanthan gum, a polyanion. The primary objective is to assess liposome stability upon interaction with these polyelectrolytes. To evaluate stability, I utilize dynamic light scattering (DLS), zeta-potential measurements, and a calcein leakage assay via fluorescence spectroscopy. When combining chitosan with a 0.25 mg/mL solution of liposomes, a substantial increase in measured effective diameter was observed from 1 ppm to 10 ppm chitosan. In contrast, xanthan gum does not induce a significant change in effective diameter within the same concentration range. The calcein leakage assay provided additional confirmation for the interaction of liposomes and chitosan and lack thereof for liposomes and xanthan gum. This difference is attributed to the negative zeta-potential surrounding bare liposomes, which facilitates stronger electrostatic interactions with the positively charged chitosan compared to the negatively charged xanthan gum. Additionally, calculation of the number of charged groups per mass of each polyelectrolyte shows that xanthan gum has 2.5 times more charge density than chitosan, further amplifying its charge repulsion with liposomes.